Serializing objects to file
A standard way to serialize R objects to file is to use saveRDS() and readRDS().
A number of standard compression schemes are offered withni saveRDS() in order to save disk space,
I’ve swiped some benchmarks from here
and pulled out the numbers corresponding to the default options in R
gzip- fast, but no very efficient
- Default compression level in
gzfile(): 6 - Compression/decompression speeds: 19 MB/s and 95 MB/s respecively
bzip2- slower than gzip, but better compression
- Default compression level in
bzfile(): 9 - Compression/decompression speeds: 7 MB/s and 24 MB/s respecively
xz- very very slow. great compression
- Default compression level in
xzfile(): 6 - Compression/decompression speeds: 1.4 MB/s and 53 MB/s respecively
New compression algorithms - LZ4 and Zstandard
LZ4 and Zstandard are two recent compression schemes. Both are very fast and
highly configurable in terms of the compression/speed tradeoffs they offer.
Because they’re not benchmarked on the same corpus, the compression/decompression speeds should be compared with caution, but they’re both easily an order of magnitude faster than gzip/bzip2/xz.
The archive package
jimhester has a work-in-progress package called
archive which is a wrapper around the very
capable libarchive.
The archive package then lets you create
standard R connection objects that do inline compression of the data using
libarchive. You can then use these connection objects in any file function
that supports them e.g. saveRDS(), write.csv.
libarchive itself supports a very wide range of archvie formats and compression schemes including:
- zstd
- lz4
- zip
- rar
- lzip
- lzma
- tar
- lha
- 7-zip
saveCRDS() and readCRDS() - writing R objects with compression
In order to support writing compressed archives, I’ve written two simple wrapper
function which initialise a compressed connection and then use that with R’s
builtin serialisation functions (saveRDS() and readRDS()).
Currently there can be some flakiness with archive when specifying formats/filters that aren’t
supported by the current compiled version of libarchive. This can cause
segfaults, so I’m being extra paranoid about the formats/filters supported.
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
#' Write compressed RDS streams
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
saveCRDS <- function(object, filename, filter=NULL) {
stopifnot(filter %in% c('zstd', 'lz4'))
con = archive::file_write(file = filename, filter=filter)
open(con)
saveRDS(object, con)
close(con)
}
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
#' Read compressed RDS streams
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
readCRDS <- function(filename) {
con <- archive::file_read(file = filename)
res <- readRDS(con)
close(con)
res
}Saving a compressed version of a 10 MB low complexity matrix
- Testing on highly compressible test data
N <- 3200
test_data <- matrix(sample(as.raw(c(0, 0, 1)), size=N*N, replace=TRUE), nrow=N, ncol=N)
pryr::object_size(test_data)Registered S3 method overwritten by 'pryr':
method from
print.bytes Rcpp10.2 MBtest_dir <- tempdir()
res <- bench::mark(
saveRDS (test_data, file = file.path(test_dir, "test.rds" ), compress = FALSE),
saveRDS (test_data, file = file.path(test_dir, "test.rds.gz" ), compress = 'gzip'),
saveRDS (test_data, file = file.path(test_dir, "test.rds.bz2" ), compress = 'bzip2'),
saveRDS (test_data, file = file.path(test_dir, "test.rds.xz" ), compress = 'xz'),
saveCRDS(test_data, filename = file.path(test_dir, 'test.rds.lz4' ), filter='lz4'),
saveCRDS(test_data, filename = file.path(test_dir, 'test.rds.zstd'), filter='zstd'),
min_time=2, check = FALSE
)| compression | filesize (MB) | median time (s) | itr/sec | mem_alloc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uncompressed | 10.24 | 15.6ms | 60.07 | 28.2KB |
| gzip | 1.60 | 1.5s | 0.67 | 8.63KB |
| bzip2 | 1.52 | 851.4ms | 1.17 | 11.59KB |
| xz | 1.29 | 13.8s | 0.07 | 11.59KB |
| lz4 | 4.90 | 45.6ms | 22.03 | 46.4KB |
| zstd | 1.94 | 59.7ms | 16.42 | 3.38MB |
The following is a plot of the bench::mark() results on this data, with
compressed filesize on the x-axis, and the median compression time (in seconds)
on the y-axis (on a log scale).
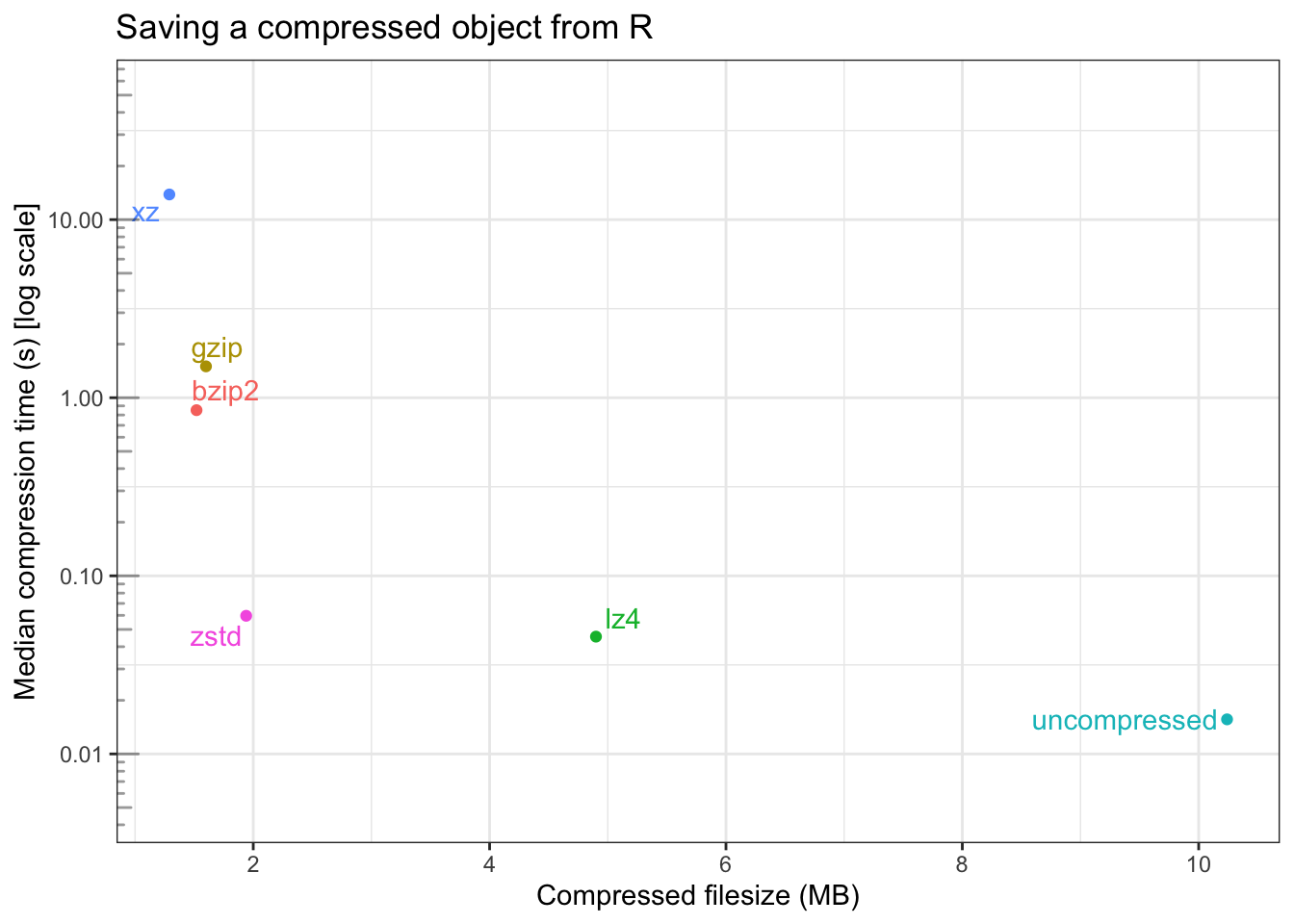
On this data, running on my machine, it appears:
- uncompressed data is saved in about 100th of a second
- to a first approximation,
xz,gzip,bzip2andzstdall compress to roughly the same size (with their default compression levels) lz4has the largest compressed filesize, but the fastest speedxzhas the smallest compressed filesize, but by far the longest compression time- Compare to writing the uncompressed data
lz4andzstdare 3-5x slowerbzip2andgzipare ~2 orders of magnitude slowerxzis ~3 orders of magnitude slower
Future
- Expand the tests to cover more data sizes, and more complex data.
- There’s no configuration of LZ4/Zstandard compression options in
archiveyet, so there’s a whole range of time/compression tradeoffs that are currently unavailable using these compression methods.