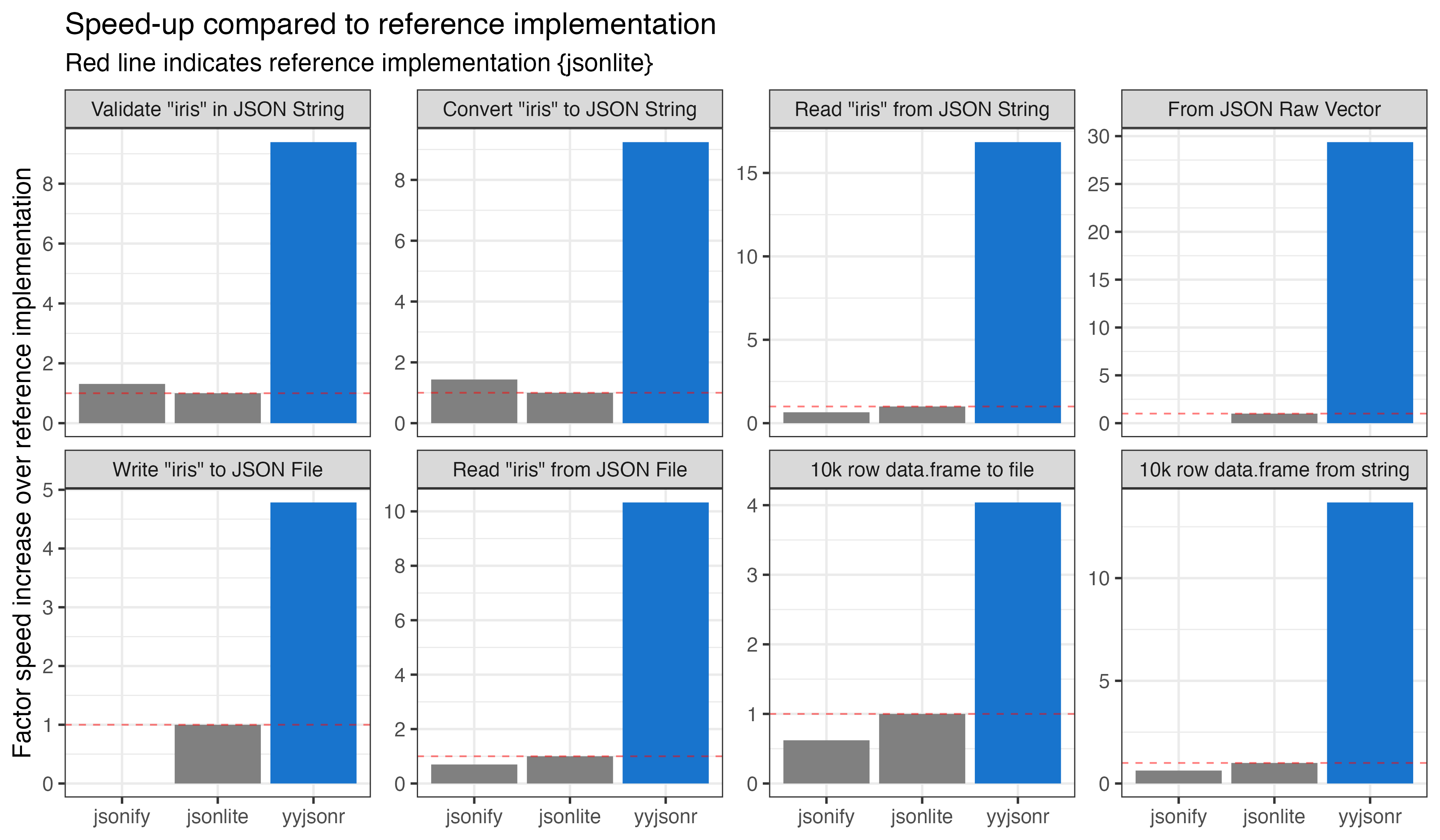
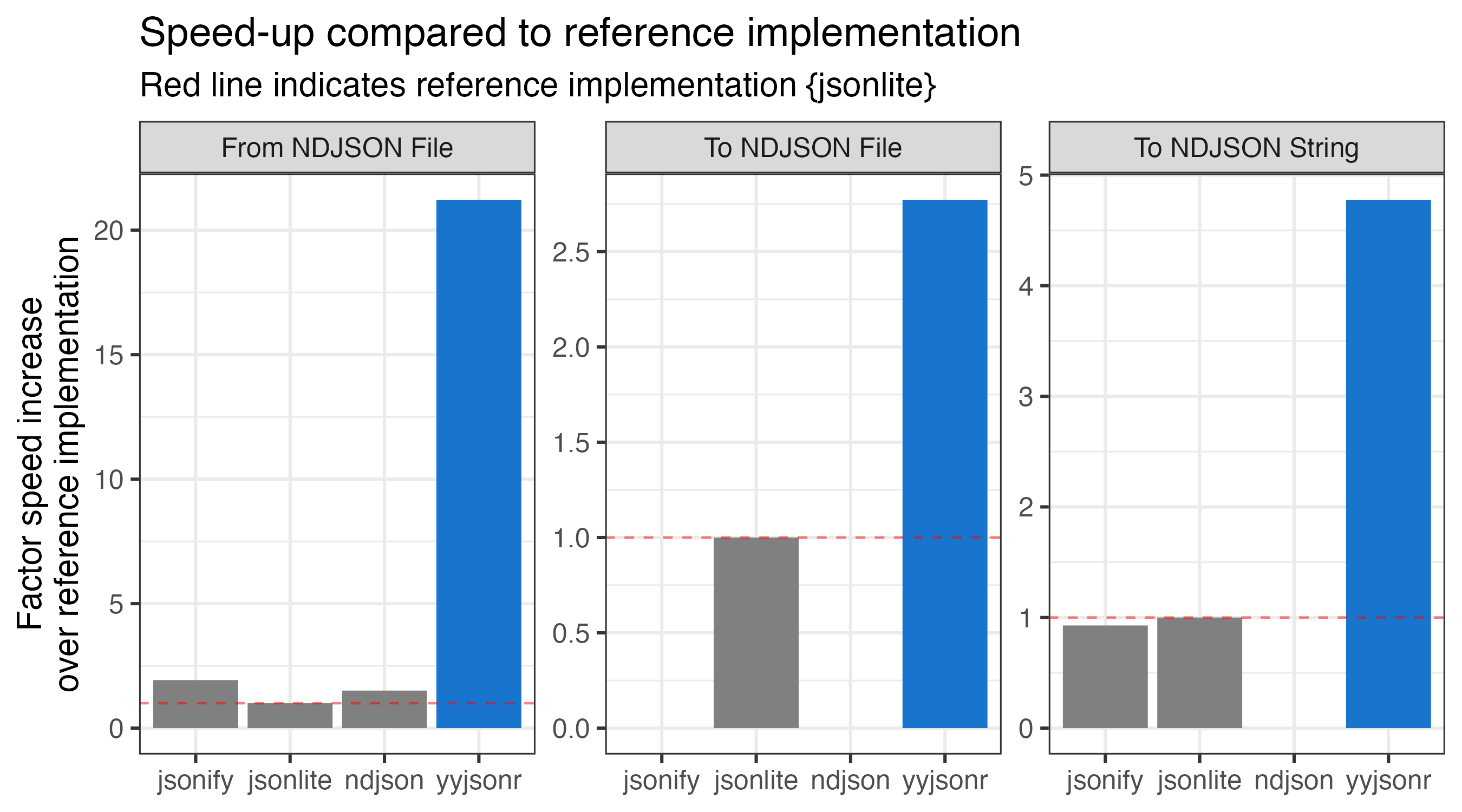
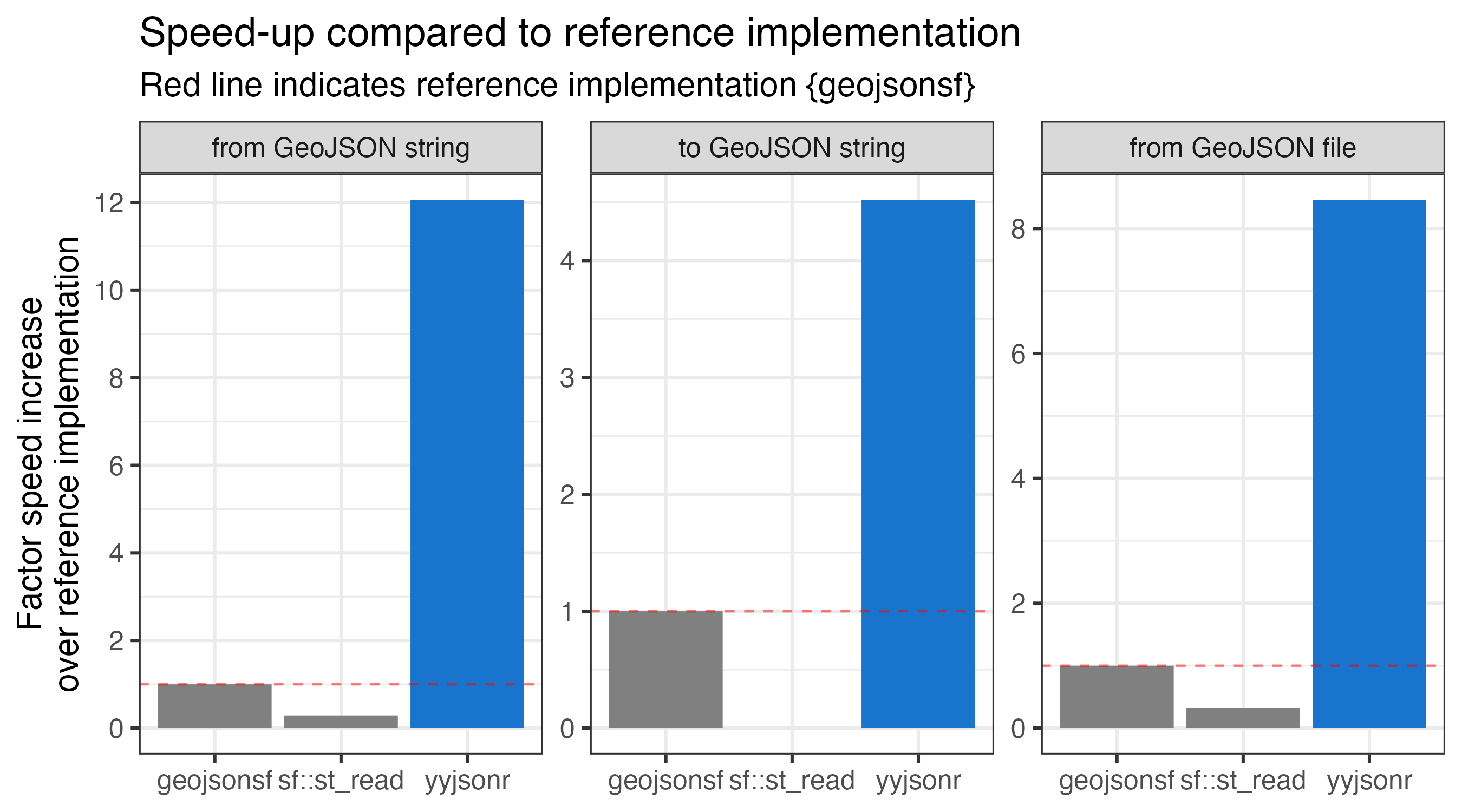
yyjsonr 
yyjsonr is a fast JSON parser/serializer, which converts R data to/from JSON.
In most cases it is around 2x to 10x faster than jsonlite at both reading and writing JSON.
It is a wrapper for the yyjson C library (v0.8.0). yysjon is MIT licensed - see LICENSE-yyjson.txt in this package for more details.
What’s in the box
This package contains specialized functions for each type of operation (read/write/validate) and the storage location of the JSON (string/file/raw vector/connection).
Vanilla JSON
| string | file | raw | conn | options | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| read | read_json_str() | read_json_file() | read_json_raw() | read_json_conn() | opts_read_json() |
| write | write_json_str() | write_json_file() | opts_write_json() | ||
| validate | validate_json_str() | validate_json_file() |
Installation
You can install from GitHub with:
# install.package('remotes')
remotes::install_github('coolbutuseless/yyjsonr')Simple JSON example
library(yyjsonr)
str <- write_json_str(head(iris, 3), pretty = TRUE)
cat(str)
#> [
#> {
#> "Sepal.Length": 5.1,
#> "Sepal.Width": 3.5,
#> "Petal.Length": 1.4,
#> "Petal.Width": 0.2,
#> "Species": "setosa"
#> },
#> {
#> "Sepal.Length": 4.9,
#> "Sepal.Width": 3.0,
#> "Petal.Length": 1.4,
#> "Petal.Width": 0.2,
#> "Species": "setosa"
#> },
#> {
#> "Sepal.Length": 4.7,
#> "Sepal.Width": 3.2,
#> "Petal.Length": 1.3,
#> "Petal.Width": 0.2,
#> "Species": "setosa"
#> }
#> ]
read_json_str(str)
#> Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
#> 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
#> 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
#> 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosaSimple GeoJSON example
When parsing GeoJSON, yyjsonr returns an sf object.
read_geojson_str(geojsonsf::geo_melbourne) |>
head() |>
sf:::print.sf()
#> Simple feature collection with 6 features and 7 fields
#> Geometry type: POLYGON
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 144.8958 ymin: -37.86631 xmax: 145.0371 ymax: -37.75423
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> SA2_NAME polygonId SA3_NAME AREASQKM fillColor
#> 1 Abbotsford 70 Yarra 1.7405 #440154
#> 2 Albert Park 59 Port Phillip 4.6747 #450457
#> 3 Alphington - Fairfield 41 Darebin - South 2.8853 #46075A
#> 4 Armadale 66 Stonnington - West 2.1835 #460A5D
#> 5 Ascot Vale 44 Essendon 3.8361 #460C5F
#> 6 Brunswick 36 Brunswick - Coburg 5.1425 #472D7B
#> strokeColor strokeWeight geometry
#> 1 #440154 1 POLYGON ((144.9925 -37.8024...
#> 2 #450457 1 POLYGON ((144.9449 -37.8437...
#> 3 #46075A 1 POLYGON ((145.0204 -37.7654...
#> 4 #460A5D 1 POLYGON ((145.0117 -37.8535...
#> 5 #460C5F 1 POLYGON ((144.8994 -37.7704...
#> 6 #472D7B 1 POLYGON ((144.9497 -37.7627...