ingrid provides some tools that I find useful for creating/manipulating grid/grob.
The key benefits I get from ingrid:
-
nested layout
rowandcol- similar to shiny UI definition -
consistent interface to grob combination functions (intersection, union etc) which work across
grobs,gTreesandpolyclipgrobs -
verbose
printmethods for grobs - inline graphical parameter specification
- Global, user-configurable
default.units
Todo
- igt translate and rotate could work on both grobs and viewports?
What’s in the box
-
ig_*()grob creation functions with inlinegparspecification- e.g.
ig_circle(r = .mm(10), fill = 'blue')
- e.g.
-
igc_*()grob combination operators -
igl_*()layout for multiple grobs -
igt_*()transform operations on grobs-
igt_translate(),igt_rotate() -
igt_update()to update any parameter in the grob or viewport
-
Click here to reveal more details on what’s included
-
ig_circle()etc. Analoges for the the grob creation functions in thegridpackage, but with a slight change in the argument defaults:- default.units are now ‘mm’ instead of ‘npc’
- the
gpandvpobjects are both created as fully realised structures, and no longer left asNULLif no values are given. This makes manipulation of grob objects a bit easier after they’ve been created.
- Set of functions for combining vanilla grobs, polyclipgrobs and gTree objects. These functions are mostly extensions of
gridGeometry::polyclipgrob()which extends the operations to recurse into gTree and polyclipgrob structures to affect all child objects:-
igc_stack()for simple combination of shapes -
igc_intersect()for shape intersection -
igc_union()for shape union -
igc_minus()for shape subtraction -
igc_xor()for shape combination thruogh use of ‘exclusive or’
-
- Functions for creating units quickly e.g
.mm(x)instead ofunits(x, 'mm') - Verbose printing of vanilla grob, gTree and polyclipgrob objects
- Structured printing of the grid pattern objects available in R4.1.0
- Simple grob coordinate transformations:
- Simple viewport transformations:
vp_translate()vp_rotate()
-
gp()is a wrapper aroundgrid::gpar()which is more friendly for IDEs which support auto-complete. - Some helpers for patterns:
- S3
printmethods with more structured output thangrid’s default -
ig_pattern()is a wrapper aroundgrid::pattern()where:-
extend = 'repeat'is the default (instead of ‘pad’) -
default.unitsare in ‘mm’ (instead of ‘npc’) - location coordinates (x, y) are offset from the centre of the viewport by default. Set
centred = FALSEto disable this behaviour.
-
- S3
Installation
You can install from GitHub with:
# install.package('remotes')
remotes::install_github('coolbutuseless/ingrid')Nested object specification
ingrid reframes the grid layout functions into nested hierarchical layout functions, somewhat similar to how shiny does it’s UI layout.
-
igl_row()will arrange its sub-elements in a horizontal row. -
igl_col()will arrange its sub-elements in a vertical column. -
igl_vp()will create an arbitrary viewport containing its sub-elements.
check <- igl_row(
igl_col(
ig_rect(fill = 'black'),
nullGrob()
),
igl_col(
nullGrob(),
ig_rect(fill = 'black')
)
)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(check)
check45 <- igl_vp(check, angle = 45)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(check45)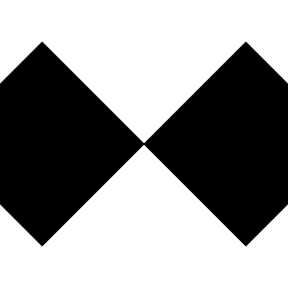
demo <- igl_row(
ig_rect (fill = ig_pattern(check , width = .cm(1.5), height = .cm(1.5))),
ig_circle(fill = ig_pattern(check , width = .cm(2.5), height = .cm(2.5))),
ig_rect (fill = ig_pattern(check45, width = .cm(3 ), height = .cm(3 )))
)
grid::grid.newpage(); grid::grid.draw(demo)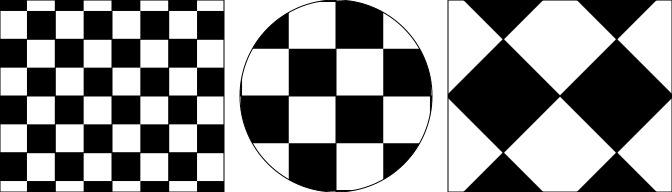
Combining grobs
Grobs may be combined with igc_*() functions.
-
igc_stack()combines multiple grobs (as agrobTree() -
igc_intersetion(),igc_union(),igc_xor()andigc_minus()are general set operations on grobs usinggridGeometry::polyclipGrob() -
igc_combine()is the core function used by the above set operators -
igc_mask()andigc_clip()use the new arbitrary clip and mask functionality introduced in R4.1
library(grid)
library(ingrid)
wug <- igc_intersect(
igc_stack(
ig_circle(r = .mm(20), fill = 'red', alpha = 0.3),
ig_circle(r = .mm(33), x = .mid + .mm(25), fill = 'blue', alpha = 0.3),
ig_circle(r = .mm( 2), x = .mid - .mm(13), y = .mid + .mm(4), fill='black', col='white')
),
ig_circle(r = .mm(28), x = .mid - .mm(19), y = .mid - .mm(20), fill = 'lightblue', col = 'transparent', alpha = 0.3)
)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(wug)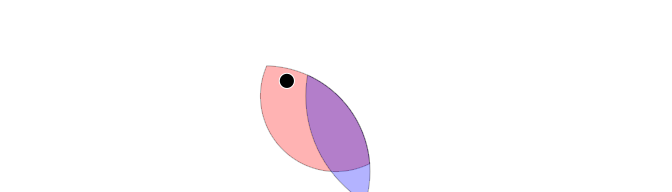
Masking
igc_mask() and igc_clip() use the new arbitrary clip and mask functionality introduced in R4.1
library(grid)
library(ingrid)
# Hex
r <- .mm(20)
theta <- seq(30, 360, 60) * pi/180
x <- .mid + .mm(r * cos(theta))
y <- .mid + .mm(r * sin(theta))
hex <- ig_polygon(x, y, fill = 'blue')
# Random raster
ras <- ig_raster(
image = matrix(runif(100), 10, 10)
)
# Draw individually
grid.newpage()
grid.draw(ras)
grid.draw(hex)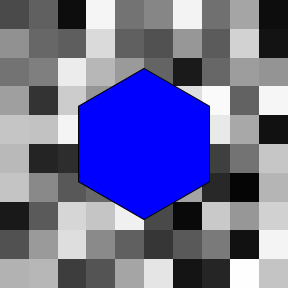
# Mask the raster with the hex
masked <- igc_mask(ras, hex)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(masked)
Transform grobs by translation/rotation
# Template object that will be adapted
rect <- ig_rect(width = .cm(2), height = .cm(2), col = 'grey20')
# create grobs
N <- 160
color <- rainbow(N)
grobs <- lapply(seq(N), function(i) {
igt_translate(
x = -.mid + .mm(3 * i),
y = .inch(sin(i/4)),
igt_rotate(
angle = i * 2,
igt_update(rect, fill = color[i])
)
)
})
# draw
grobs <- do.call(grid::grobTree, grobs)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(grobs)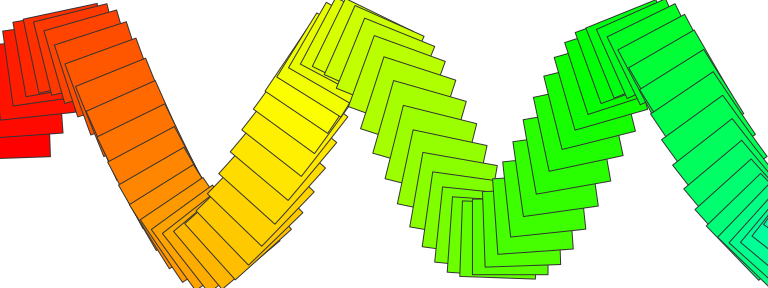
# Template object that will be adapted
rect <- ig_rect(width = .cm(1), height = .cm(1), col = 'white')
N <- 160
color <- rainbow(N)
# Coords
r <- .mm(40)
theta <- (seq(0, 360, length.out = N + 1) * pi/180 )[-1]
x <- .mm(r * cos(theta + 0.2) + r * sin(3 * theta))
y <- .mm(r * 0.8 * cos(2 * theta) + r * sin(theta))
# create grobs
grobs <- lapply(seq(N), function(i) {
igt_translate(
x = x[i],
y = y[i],
igt_rotate(
angle = i * 5,
igt_update(rect, fill = color[i])
)
)
})
# draw
grobs <- do.call(grid::grobTree, grobs)
grid.newpage(); grid.draw(grobs)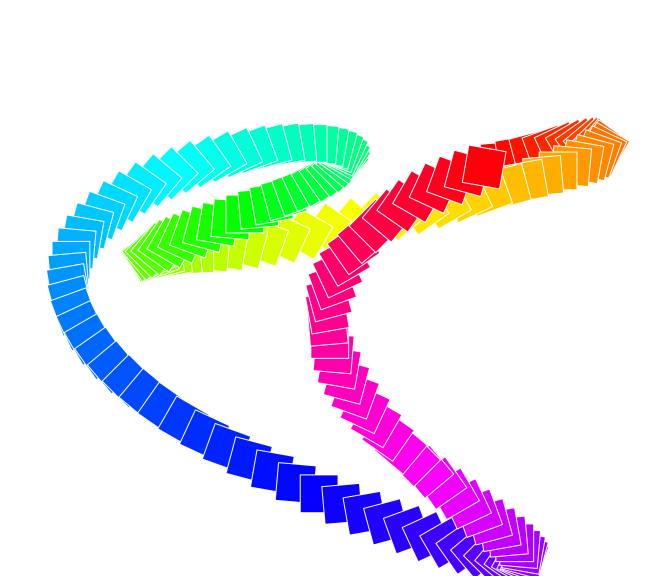
Future
- Include grobs from other sources:
-
ellipseGrob,ngonGrobfrom gridExtra
-
Related Software
- gridExtra
- grid - part of R
- gridGeometry
- polyclip